Uruguay leads the world in environmental change because its leaders selected economic strategies instead of following political dogma. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) performed research which revealed Uruguay achieved top twenty environmental leadership status through its adoption of renewable energy because of its affordable benefits.
Choosing Renewables for Economic Strength
Just two decades ago, Uruguay relied heavily on imported fossil fuels. The country imported oil at a rate of 30 percent from its total imports which mostly originated from Argentina. The economic system became exposed to market price changes and supply disruptions because of this interconnection.
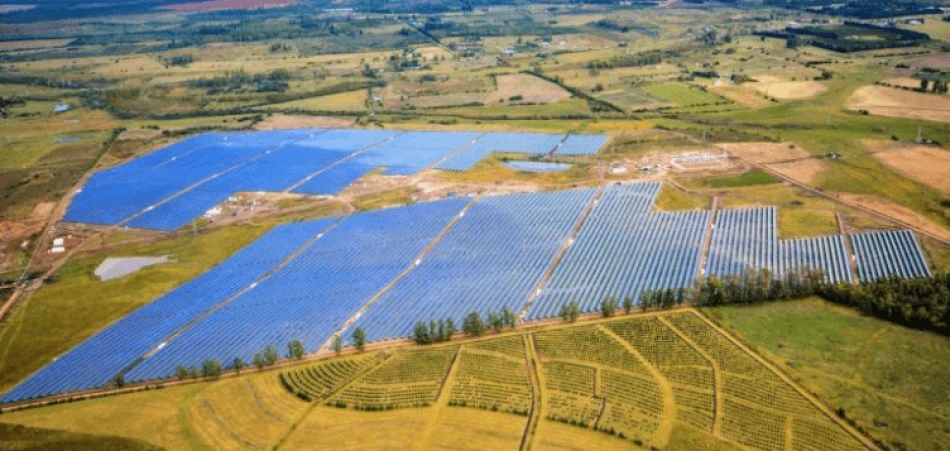
Uruguay implemented a fundamental transformation of its healthcare system during the period from 2010 to 2016. The government dedicated $7.8 billion to update its energy infrastructure by building new renewable power systems. The country generated 97 percent of its electricity from renewable sources during 2019 which proved to be an outstanding renewable energy performance compared to worldwide benchmarks.
The power sector of Uruguay started its fast-paced evolution during the previous decade when officials recognized wind power and additional renewable energy sources as effective solutions to decrease electricity generation expenses. Rebecca Bertram of EnergyTransition.org explains that Uruguay achieved success through its practice of open decision-making and its favorable business environment and its successful partnership between government agencies and private funding sources.
The current electricity production in Uruguay exceeds domestic requirements so the country exports its excess power to surrounding nations. By 2017, the nation had reduced its greenhouse gas emissions by an impressive 88 percent compared to the 2009–2013 average.
Geography That Supports Clean Energy
The natural environment of Uruguay serves as a key factor which enables the country to achieve success in renewable energy production. The nation has a flat landscape with eight miles per hour wind speeds and its borders extend along the Atlantic Ocean and major rivers. The country has suitable environmental conditions for power generation because it supports wind energy and solar power and hydropower systems.
The country now stands as a global wind energy leader together with Denmark and Ireland and Germany. The total electricity production of these countries depends on wind power for more than one-third of their output.
One of the Americas’ Few Green Leaders
The international community has observed Uruguay's progress because they have seen its development success. The 2021 Green Future Index from MIT Technology Review Insights placed Uruguay at number 20 among global environmental performers which established the country as one of the top environmental performers worldwide.
The Green Future Index assesses 76 nations through their sustainable development achievements by analyzing their performance in carbon reduction and energy transformation and their progress in green technology and environmental regulations and their ability to create sustainable communities.
Uruguay is one of only three countries in the Americas—alongside Costa Rica and Canada—to rank in the global top twenty. The majority of other leading countries are based in Europe.
The energy transition ranking of Uruguay reached 10th position because the country experienced fast renewable energy expansion which became a major component of its total energy production. The ranking system placed this organization at number 10 for clean innovation because it demonstrated excellent ability to create and use sustainable environmental technologies.
A Model for the World
The Uruguayan case demonstrates that environmental protection and economic growth establish interconnected systems which enhance each other. The nation built a sustainable energy system through renewable power adoption because it brought both operational benefits and economic advantages. The nation built an environmentally friendly power grid which serves as a successful model for countries seeking to reach sustainable development while fighting climate change.